The darknet, also known as the dark web, is a concealed section of the internet that's inaccessible via standard search engines. You can only access it using special software, settings, or authorization. This area comprises websites and content that are purposely kept hidden from public view.
Accessing darknet requires using Tor Browser, a special web browser that routes your internet traffic through a global network of relays managed by volunteers. This way, it becomes very difficult to trace which websites you're visiting, and these sites won't know where you are located.
When visiting the dark web, use a secure browser like Tor, do not reveal any of your personal information, and don't open suspicious files or links to stay safe.
The Darknet is often utilized for secure communication, discreet information or file sharing, anonymous research without identity exposure, and occasionally for engaging in illicit activities. It is also recognized for hosting underground black markets(darknet markets), whistleblowing platforms, and discussion boards that champion freedom of speech.
While accessing Darknet Markets themselves is typically not against the law in most places, engaging with illicit goods within them is generally considered a crime. On the other hand, some people might visit Darknet Markets for lawful purposes such as research, journalistic work, or simply to explore online communities. It's essential to know the local laws regarding online activities, and be cautious when using these platforms to avoid any potential issues.
Germany Closes 47 Crypto Exchanges Linked to Criminal Activities
Germany, once home to some of the largest Bitcoin treasuries, has shut down several crypto exchanges. It claims they were used by cybercriminals. This is one of the biggest crackdowns on exchanges in history.
On Thursday, the Public Prosecutor General's Office revealed the closures. The government's Central Office for Combating Cybercrime (ZIT) and the Federal Criminal Police Office (BKA) carried them out.
Intentional Actions Leading to Seizure
The now-closed exchange services' operators are accused of a major crime. They allegedly failed to implement anti-money laundering laws, especially the KYC principle. This allowed them to hide the source of illegally acquired funds. This negligence allegedly allowed them to evade money laundering regulations and to run illicit trading platforms online, according to a translation of the Public Prosecutor General's Office's press release from Thursday.
German authorities further alleged that the closed crypto exchanges facilitated transactions without proper registration and the implementation of KYC measures.
"The services were designed for a quick, easy, and anonymous exchange of cryptocurrencies for other digital currencies. This would hide their origins," the press release said.
In addition to banning the exchanges in the German internet space, IT systems and other related data were confiscated as part of the investigation into the local darknet.
In a separate statement, the BKA noted that the shutdown of crypto exchanges aims to "weaken and dismantle the infrastructure of cybercriminals." They have drained funds from the underground economy.
Veteran Exchange Among Those Shut Down
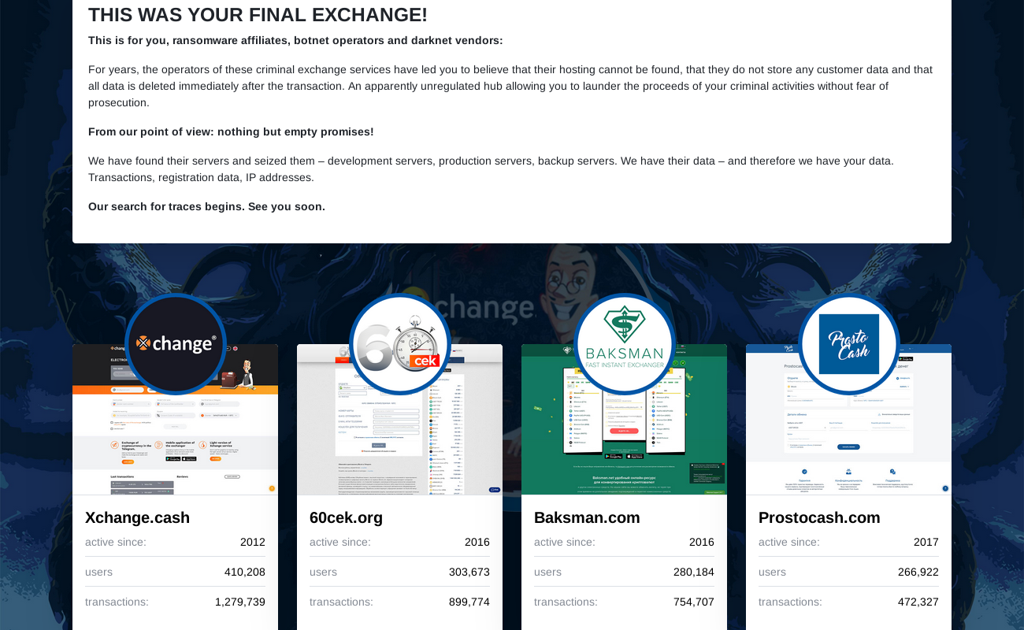
To combat crime on crypto platforms, the German government closed several exchanges, including Xchange.cash. Details are on a dedicated awareness website.
Founded in 2012, Xchange.cash boasted over 400,000 users and facilitated more than 1.2 million transactions.
Additionally, the crackdown targeted other exchanges such as 60cek.org, Baksman.com, and Bankcomat.com, all of which launched in 2016. Furthermore, several recently established exchanges were also affected, including CoinBlinker.com, Cryptostrike, DotSatoshi.com, and BTCWorm.com.
Germany: The Former Bitcoin Giant
Germany recently decided to tighten rules on crypto exchanges. This came after it liquidated its $3 billion Bitcoin reserve, seized from the piracy site Movie2k.to in 2020. The European country sold off its substantial BTC holdings from June to July, ultimately disposing of all 50,000 Bitcoins. This sell-off sparked fear, uncertainty, and doubt (FUD) in the crypto community. It caused Bitcoin prices to drop at times.
As a proponent of international digital asset regulation, Germany has been vocal in its calls for a collaborative framework to combat fraud and other issues reminiscent of the circumstances that led to the FTX collapse, as advocated by its financial regulator, BaFin.
